By Des Nnochiri
Over the last decade, cloud computing has revolutionized the way we handle and store data, which has, in turn, paved the way for greater innovations in technology. What can we expect from cloud computing as the technology advances?
IBM’s Purchase of Red Hat
On Sunday, October 28, 2018, tech giant IBM announced that they were purchasing Red Hat![]() , the open software that currently partners with many of IBM’s biggest competitors, including Google, Amazon, and Microsoft. The deal is set to be finalized in early 2019.
, the open software that currently partners with many of IBM’s biggest competitors, including Google, Amazon, and Microsoft. The deal is set to be finalized in early 2019.
This will be one of the biggest ever technological collaborations, with minds from some of the largest software companies in existence coming together to produce a hybrid cloud. Hybrid clouds are computing environments that allow data to be transferred across private and public clouds that are typically isolated from each other.
Cloud systems are extremely useful, but up until now they have been difficult to integrate with other systems. This is largely due to the fact that the companies specializing in cloud computing—again, Google, Amazon and Microsoft—purposefully secluded themselves to avoid sharing the spotlight.
It is also because the first incarnation of any new software tends to be very specified, and it’s difficult to predict on the outset what the scope will be. However, now that these software giants are going to be connected through Red Hat and working under a common name—IBM—we should see an emergence of new applications and better integration.
Growth
As more businesses move to cloud-based storage systems and the companies building them see a greater ROI, consumers should see a drop in prices. This would undoubtedly attract more people to the cloud, with the increased revenue and interest spawning yet more developments. As previously stated, the full potential of cloud computing has yet to be realized.
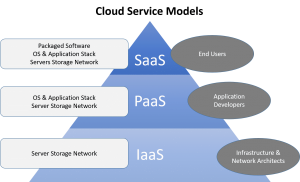
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS), platform as a service (PaaS) and database as a service (DBaaS) are relatively new offerings which have increased the number of available personal and business cloud solutions. As well as an expansion in the variety of cloud systems, storage limits continue to increase even as prices fall, and these trends will likely continue under the control of IBM and their new partners.
Smaller Hardware
Much like CDs replaced floppy disks, cloud storage could eventually make physical storage devices irrelevant. SD cards are already shrinking away to nothing, and computer hard drive disks are being replaced with smaller, smoother solid state drives. But as cloud storage increases, more of the disk space is going unused. The portability of cloud-based storage far outstrips that of even pen drives and CDs and removes the need for physical devices which can be easily damaged in transit.
Eventually, hardware such as phones, TVs, and gaming consoles may only require enough physical storage for their operating systems and a processor, and everything else is backed up to the cloud. This would result in smaller, even more portable devices, and past fads like Google Glass![]() could even make a comeback.
could even make a comeback.
Security
With so many of us storing our lives digitally, it can feel as though we are more vulnerable than ever. While it’s true that 2017 and 2018 saw a huge spike in cyber-attacks![]() , we learn more about cyber security each time and the cloud storage systems get stronger as a result.
, we learn more about cyber security each time and the cloud storage systems get stronger as a result.
Security will inevitably be an issue in computing of any kind, but one benefit of cloud computing remaining in the control of businesses with limitless R&D budgets is that they will always improve their defenses. Some companies have begun to explore the possibility of implementing blockchain technology in cloud computing in order to improve transparency in user activity, which will help to prevent fraudulent transactions.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology was originally introduced as a form of online banking for cryptocurrency, but it has the ability to process virtually any type of transaction. Blockchain developers have realized its potential to function as a new form of internet, with the added security benefit of being completely decentralized – hosted by millions of computers simultaneously![]() , much like the cloud.
, much like the cloud.
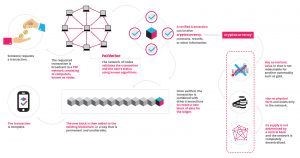 iExec
iExec![]() —a company based in Lyon, France—is a big name in Blockchain technology. In May 2018, they demonstrated their decentralized cloud alongside Intel SGX (Software Guard Extensions) as a proof of concept for a new form of secure cloud computing.
—a company based in Lyon, France—is a big name in Blockchain technology. In May 2018, they demonstrated their decentralized cloud alongside Intel SGX (Software Guard Extensions) as a proof of concept for a new form of secure cloud computing.
Intel SGX is a Trusted Execution Environment (TEE) that allows sections of code and specified data to be processed in isolated areas of a processor called “enclaves”. Enclaves create secure “bubbles” on a host machine, and even the root admins for the host machine are unable to inspect or interfere with the application they contain.
The successful demonstration in May proved this to be a viable solution to cloud security concerns. On October 29, 2018, iExec released a user guide![]() for their end-to-end trusted execution solution, which provides comprehensive protection for blockchain computing.
for their end-to-end trusted execution solution, which provides comprehensive protection for blockchain computing.